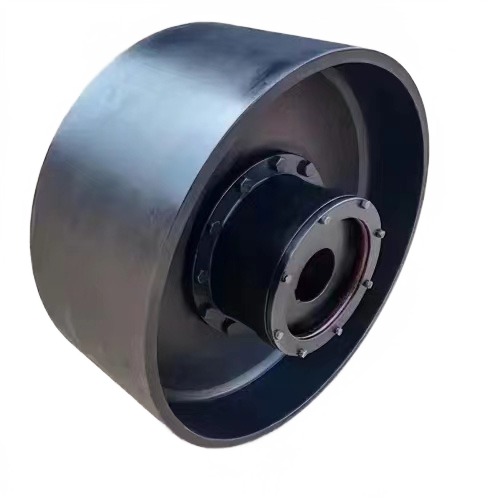
When the drum shaped gear coupling with brake wheels is in operation, the two axes produce relative angular displacement, and the tooth surfaces of the inner and outer teeth periodically slide axially, inevitably resulting in tooth surface wear and power consumption. Therefore, the gear coupling needs to work in a good and sealed state. Toothed couplings have small radial dimensions and large load-bearing capacity, and are commonly used for shaft transmission under low-speed and heavy-duty working conditions. Toothed couplings with suitable accuracy and dynamic balance can be used for high-speed transmission, such as shaft transmission in gas turbines
The drum gear coupling with brake wheel is composed of internal gear rings with the same number of teeth and flange half couplings with external teeth. The external teeth are divided into two types of tooth shapes: straight teeth and drum teeth. The so-called drum teeth refer to the spherical shape of the external teeth, with the center of the spherical surface on the gear axis. The tooth side clearance is larger than that of ordinary gears. The drum tooth coupling can allow for larger angular displacement (relative to the straight tooth coupling), which can effectively improve the contact conditions of the main teeth, improve the ability to transmit torque, and extend the service lifeThe so-called drum tooth refers to the spherical shape of the outer teeth, with the center of the spherical surface on the gear axis and larger tooth side clearance than ordinary gears. The drum tooth coupling can allow larger angular displacement (relative to straight tooth coupling), which can effectively improve the contact conditions of the main teeth, improve the ability to transmit torque, and extend the service life. The drum tooth coupling is a rigid flexible coupling, which is composed of internal gear rings with the same number of teeth and flange half couplings with external teeth. The outer teeth are divided into two types of tooth shapes: straight teeth and drum teeth, and the contact state along the tooth width when there is angular displacement. It has the ability to compensate for radial, axial, and angular axis deviations, and has the advantages of compact structure, small turning radius, large bearing capacity, good transmission efficiency, low noise, and long maintenance cycle. It is particularly suitable for low-speed and heavy-duty working conditions, such as metallurgy, mining, lifting and transportation industries, and is also suitable for shaft transmission of various types of machinery such as petroleum, chemical, and general machinery. When working, the tooth coupling generates relative angular displacement between the two axes, and the tooth surfaces of the inner and outer teeth periodically slide axially, inevitably resulting in tooth surface wear and power consumption. Therefore, the tooth coupling needs to work in a good and sealed state. Toothed couplings have small radial dimensions and large load-bearing capacity, and are commonly used for shaft transmission under low-speed and heavy-duty working conditions. Toothed couplings with suitable accuracy and dynamic balance can be used for high-speed transmission, such as shaft transmission in gas turbines. Reminder: The drum shaped gear coupling belongs to the rigid flexible coupling, which is composed of internal gear rings with the same number of teeth and flange half couplings with external teeth. The external teeth are divided into two types of tooth shapes: straight teeth and drum teeth. The so-called drum teeth refer to the spherical shape of the external teeth, with the center of the spherical surface on the gear axis. The tooth side clearance is larger than that of ordinary gears. The drum tooth coupling can allow for larger angular displacement (relative to the straight tooth coupling), which can effectively improve the contact conditions of the main teeth, improve the ability to transmit torque, and extend the service life